Surgical instruments are an essential component of any medical procedure, providing surgeons with the necessary precision and control to achieve successful outcomes. One such specialized tool is Viterbo’s surgical instrument which is designed to aid in delicate and intricate procedures. While not as widely recognized as other common surgical tools, the Viterbo instrument plays a crucial role in specific types of surgeries, particularly in plastic, reconstructive, and microsurgery. Its unique design and application make it a valuable tool in modern surgical practice.

Design and Features of Viterbo’s Surgical Instrument
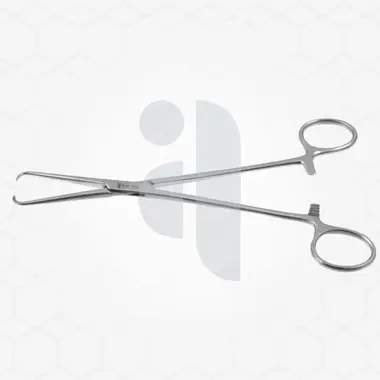
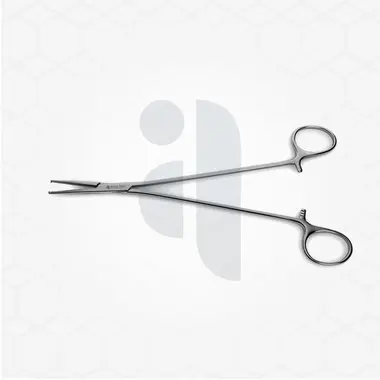
Viterbo’s surgical instrument is crafted to offer superior precision and control, allowing for meticulous surgical interventions. It is typically made from high-quality stainless steel, ensuring durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of sterilization. The instrument is designed with an ergonomic structure that enables the surgeon to handle it comfortably without excessive strain, which is particularly important during long and complex procedures.
The shape and size of the instrument may vary depending on the specific surgical application, but it is generally fine-tipped to allow for detailed work on soft tissues, nerves, and delicate structures. The carefully engineered design helps in reducing tissue trauma while providing maximum efficiency in handling and maneuverability.
Applications of Viterbo’s Surgical Instrument
Viterbo’s instrument is predominantly used in plastic and reconstructive surgery, where precision is critical in shaping and restoring body structures. It is particularly useful in procedures involving skin grafting, flap surgeries, and microsurgical techniques where delicate handling of tissues is required.
In microsurgery, which involves working on extremely small anatomical structures such as blood vessels and nerves, the Viterbo instrument offers the necessary control for delicate suturing and dissection. This makes it an invaluable tool in procedures like nerve repairs, replantation of amputated digits, and vascular surgeries where even the slightest miscalculation can affect surgical success.
Additionally, the instrument is used in general surgery and otolaryngology for fine dissection and manipulation of soft tissues. Surgeons rely on it for procedures requiring high precision, such as facial reconstructive surgeries, eyelid corrections, and delicate ear and nasal surgeries.
Advantages of Using Viterbo’s Surgical Instrument
One of the main advantages of Viterbo’s surgical instrument is its precision. The finely crafted tip and lightweight design allow for accurate dissection and manipulation of delicate tissues without causing unnecessary damage. This is crucial in microsurgical and reconstructive procedures, where even minimal trauma can lead to complications.
Another key benefit is its ergonomic design, which minimizes hand fatigue and enhances surgical efficiency. Surgeons performing lengthy procedures require instruments that offer a comfortable grip and easy maneuverability, and Viterbo’s instrument fulfills this need effectively.
Furthermore, the instrument’s durability and reliability make it a long-lasting addition to any surgical toolkit. Made from premium-grade materials, it is resistant to wear and tear, ensuring that it remains effective over multiple procedures. Its ease of sterilization also makes it a hygienic and safe option for repeated surgical use.
Conclusion
Viterbo’s surgical instrument is a valuable tool in modern surgery, particularly in plastic, reconstructive, and microsurgical procedures. Its precision, ergonomic design, and durability make it an essential instrument for surgeons performing delicate and intricate tasks. With its ability to enhance accuracy and minimize tissue trauma, Viterbo’s instrument continues to play a crucial role in improving surgical outcomes and patient recovery. As advancements in surgical techniques continue to evolve, the importance of such specialized instruments will only grow, further reinforcing their place in the field of medicine.






Leave a Comment