Surgical instruments are indispensable in the practice of surgery, enabling healthcare professionals to perform precise and effective procedures. These instruments are categorized based on their function, design, and the type of surgery they are used for. Understanding the various categories of surgical instruments is crucial for both surgeons and medical professionals to ensure the right tool is used for the right purpose, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
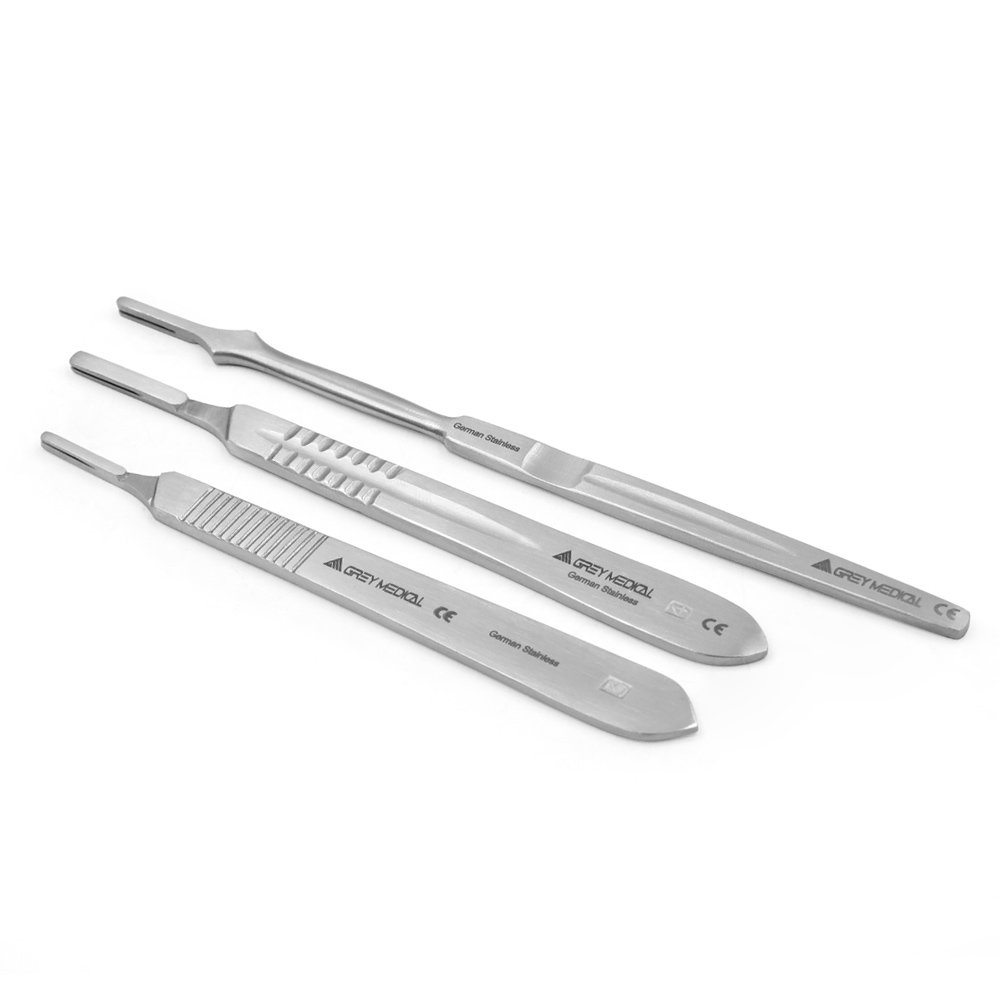

Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
Cutting and dissecting instruments are among the most fundamental tools used in surgery. These instruments are designed to make precise incisions in tissues, organs, and structures. They can range from basic scalpels to more complex cutting devices like scissors and surgical knives. Scalpels are the most commonly used cutting instruments, with handles and blades that are designed for specific surgical tasks, including precise incisions during procedures.
Scissors are another key instrument in this category, with various shapes and sizes tailored to different types of tissue. Dissecting scissors, for example, are used to separate tissues during surgery, while sharp scissors are employed for cutting through delicate or tough materials. Other specialized instruments in this category include surgical knives and bone cutting tools, which are used in more advanced procedures requiring high precision and control.
Grasping and Holding Instruments
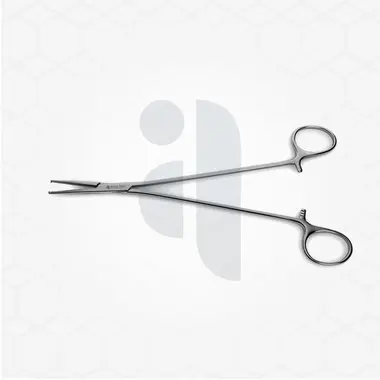
Grasping and holding instruments are designed to assist surgeons in manipulating tissues, organs, or other surgical elements during an operation. These tools provide a firm grip, allowing the surgeon to hold structures steady while working with them. One of the most commonly used instruments in this category is the forceps. Forceps come in a variety of designs, with tips that can be straight, curved, or toothed, depending on the specific need for gripping and holding.
Another essential tool in this category is needle holders, which are used to firmly grasp needles during suturing. These instruments are designed to ensure that the needle remains steady and controlled while stitching tissues together. The precise grip of these instruments is especially important in delicate surgeries, where any unintended movement can cause significant complications.
Clamping and Occluding Instruments
Clamping and occluding instruments are crucial in surgeries where it is necessary to control bleeding or to hold structures in place. These instruments work by temporarily closing off blood vessels, ducts, or tissues to prevent fluid flow, making them indispensable in procedures involving the cardiovascular or digestive systems.
Hemostats, often referred to as clamps, are commonly used to stop blood flow during surgery. These instruments are designed to apply pressure to blood vessels, tissues, or organs, controlling bleeding and providing the surgeon with a clearer view of the surgical site. There are various types of hemostats, including mosquito clamps and Kelly clamps, each designed for different sizes and types of vessels. Occlusion clamps are used similarly to restrict the flow of bodily fluids during surgical interventions, making them essential for controlling bleeding and minimizing risks.
Suturing and Stapling Instruments
Suturing and stapling instruments are essential for closing incisions and wounds after surgical procedures. These instruments help in stitching tissues back together or using staples for faster, more efficient closures.
Needle holders, as previously mentioned, are used for holding needles while performing suturing. They are available in various sizes and styles to accommodate different types of needles and suture materials. In some cases, surgeons may opt for stapling devices, which are designed to quickly and securely close wounds using staples. These staplers are particularly useful in abdominal or thoracic surgeries, where rapid closure is required to reduce surgery time and the risk of infection.
Examination and Diagnostic Instruments
Examination and diagnostic instruments are another essential category in surgery, used to inspect the patient’s condition or to assist in pre-surgical assessment. These instruments are crucial in identifying issues, determining the right surgical approach, and assisting with post-operative care.
Endoscopes, for example, are commonly used to examine internal organs and cavities. These instruments are equipped with a light source and camera, allowing surgeons to visualize the internal body structures during diagnostic or minimally invasive procedures. Similarly, surgical mirrors and diagnostic probes are often employed to assist in determining the appropriate treatment and surgical intervention.
Conclusion
Surgical instruments are integral to the successful outcome of any surgical procedure, and each category of instrument plays a vital role in ensuring precision, safety, and efficiency. From cutting and dissecting to grasping, clamping, suturing, and diagnostic tools, each instrument serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall success of the surgery. As technology and innovation continue to progress in the medical field, the evolution of surgical instruments ensures that healthcare professionals are better equipped to perform complex and delicate procedures with greater accuracy and improved patient outcomes.







Leave a Comment